Future-Proof E-commerce Business: Building a Culture of Security
E-commerce has become a dominant force in today's business landscape. This disruptive technology has transformed how we shop, offering a vast selection of products and services across nearly every industry. From everyday essentials like books and music to travel bookings and even financial services like stock trading and online banking, e-commerce platforms provide unparalleled convenience and choice for consumers.

At the heart of e-commerce lies the seamless transmission of data between consumers and sellers online. Consumers entrusted personal and financial information during transactions, making e-commerce platforms a primal target for cybercriminals. In today's digital age, data has become the new gold, and its protection is paramount for the continued success of the booming e-commerce industry.

Recent research highlights that cybercrime is on the rise for some major companies like Equifax, Yahoo, Facebook, BoAt, Cisco, etc. Almost 50% of Companies Have Been Victims of Financial Crime, According to New Thomson Reuters Report.
Aggregate losses of $1.45 trillion across surveyed companies, or 3.5% of their annual turnover, according to Revealing the True Cost of Financial Crime report. As per Statista, e-commerce losses were 41 billion US dollars due to e-commerce payment fraud in 2022, and it may reach 48 billion US dollars in 2023. If we glance at some recent happenings in this industry. An Indian consumer wearable brand boAt has suffered a massive data breach, where the personal information of more than 7.5 million customers has been compromised. The threat actor has put out around 2 Gigabytes of personally identifiable information (PII) of boAt users on dark web forums, claimed the reports.
“Customers' data being exfiltrated impacts trust and loyalty, and suppliers who rely on e-commerce ecosystems may choose to abandon the platform,” said Kumar Ritesh, Founder and CEO of CYFIRMA.
The time when data breaches are a growing concern, the breach of such an order from a brand impacts the trust and loyalty it has established with the consumers. The leakage of personal data over online forums makes consumers vulnerable to phishing and other types of scams. And the repercussions extend far beyond financial losses, as compromised data can even be used to manipulate public opinions. We will delve deeper into these risks in the following sections.
According to the Deloitte tech trends report '24, around 30 crore Indians were susceptible to online threats, and among them, an alarming 5 lakh individuals fell prey to scamsters every year.
An e-commerce firm must protect its assets from unauthorized access, use, alteration, or destruction. A secured e-commerce business should have a reliable infrastructure and framework. Experts advise that to prevent such incidents, companies need to ensure where the data is being stored and who has access to that.
Let's delve deeper.
What exactly is E-commerce security?
E-commerce security protects online transactions and information between sellers and buyers from unauthorized access, theft, and alteration.
E-commerce Security Threats
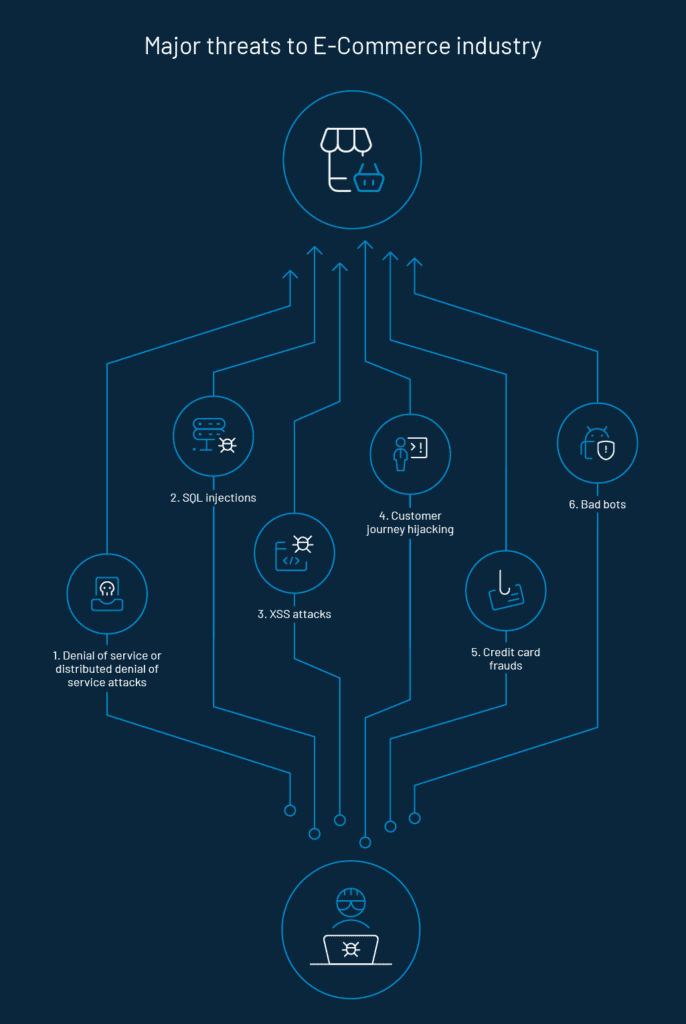
Image courtsey of loginradius.com
1. Financial Fraud: This includes various methodologies used by threat actors to steal customer payment information like billing details or exploit it for fraudulent purchases. Examples include credit card skimming, carding, face accounts, refund scams, and account takeover.
2. Data Breaches: Threat actors can exploit vulnerabilities in e-commerce platforms to gain unauthorized access to customer data like names, email addresses, contact details, and even credit card details.
3. Phishing, Vishing, and Social Engineering: Deceptive emails, fake ai-voice calls, or fake websites can trick customers into revealing personal information or login credentials.
4. Deial-of-Service (DoS or DDoS) Attacks: Bombarding an e-commerce website with overwhelming traffic that can crash even its firewalls and prevent legitimate customers from accessing the platform.
5. Malware Attacks: malicious software like viruses, spyware, Trojan horses, and ransomware can target an e-commerce platform to steal data, disrupt its supply chain operation, or hold systems hostage for ransom.
6. Insider Threats: Disgruntled employees or vendors with access to customers' data can pose a significant security risk.
7. Insecure APIs: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that are not properly secured can be exploited by hackers to gain access to sensitive data.
8. Bot Attacks: With the infallible rise of AI, malicious bots can automate tasks like account creation, product scraping, and fraudulent transactions, overwhelming systems and creating security risks.
9. E-Skimming: This is not a new devil that has been there in this market, this involves injecting malicious scripts into e-commerce payment pages to steal customer credit card information during checkout.
10. Pharming: Subset of an intelligent social engineering attempt. It is the type of cyber attack where cybercriminals redirect users to fake websites identical to the original website to get user information.
11. Whaling: Whaling, aka CEO fraud, is a type of Phishing attack where the target is high-level business executives like CEOs to receive sensitive information like financial data.
According to FBI statistics, CEO fraud is now a $26 billion scam.
Statista states that phishing, pharming, and whaling are the most common fraud types experienced by sellers in 2022.
12. Injection attacks: It is a technical attack where cyber criminals inject malicious code into an e-commerce website database to get access to users' information. For example, XSSRF, SQLi, XSSi.
By understanding these threats and implementing appropriate security measures, a firm can create a more secure e-commerce environment for its customers.
But this is not only a firm's data being compromised, privacy of a customer also gets intercepted. Having an eye on that particular side of the coin is also necessary.
Let's talk about privacy. Why it is important?
Privacy is about autonomy and control over our personal information.
In today's digital age, it's crucial to understand why privacy is so important.
Freedom of Expression: Privacy allows us to explore ideas without fear of judgment, fostering creativity and imagination.
Safety and Security: Protecting privacy prevents risks like stalking, harassment, and physical harm by controlling who has access to our information.
Control over Reputation: Privacy allows us to manage our digital image and reputation online.
But with big tech constantly compromised of data, privacy becomes even more critical. Shared data can be misused for targeted ads or exploitation by threat actors.
In the wrong hands, anonymized data can identify groups with specific interests or beliefs. This data could be used to create targeted disinformation campaigns or manipulate public opinion.
These threats can cause considerable losses to e-commerce businesses and the people trusting a firm. Yet we can protect our e-commerce organization with the following solutions.
E-commerce Security Measures:
1. Encryption: Implement strong encryption methods to protect customer data at rest (stored) and in transit (being transmitted).
2. Access Controls: Enforcement of robust controls with MFA(Multi-Factor Aunthication) and role-based access to sensitive data.
3. Data Minimization: Collect and store only a minimum amount of customer data for business operations. Fewer data to manage means a smaller attack surface.
4. Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular penetration-testing and vulnerability assessments to identify and path weaknesses in the e-commerce platform. Inviting security researchers from around the world to look onto the platforms via bug bounty platforms is a solid approach to get different areas of weaknesses and fixing. It is to ensure that your e-commerce platform provides security updates to stay away from common threats.
5. Web Application Firewalls (WAF): Implement a WAF to filter incoming traffic and block malicious requests aimed at exploiting vulnerabilities.
6. Secure Payment Gateways: Partner with reputable payment gateways like Razorpay, Juspay, etc. that utilize strong security measures to protect customer financial data.
7. Tokenization: Use tokenization to replace sensitive data like credit numbers with unique identifiers, reducing the risk of exposure if a data breach occurs. The e-commerce platform should be PCI DSS (The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliant to ensure that your credit card details are being handled securely.
8. Security Awareness Training: Train employees on cybersecurity best practices to prevent accidental data leaks, AI-powered cyber threats, and intelligent phishing attacks.
9. Incident Response Plan: Develop a well-defined incident response plan to effectively respond to mitigate data breaches.
10. Fraud Detection: Your eCommerce platform should have a fraud detection feature to identify suspicious transactions
11. SSL Certificates: By installing an SSL(Secure Sockets Layer) certificate to your website, all sensitive information of users is encrypted and protected from cyber-attacks. With a padlock icon in the address bar, the user confirms the SSL installation on your website.
We've discussed essential security measures like encryption and access controls that safeguard customer data. However, the world of cybersecurity threats is constantly evolving. That's why Information security solutions are at the forefront of innovation, leveraging cutting-edge Artificial Intelligence (AI) to further enhance its e-commerce security.
Let's explore specific AI security solutions an e-commerce organization might employ to translate a more secure shopping experience for customers and peace of mind knowing their personal information is protected.
Anomaly Detection: AI algorithms can analyze user behavior, purchase patterns, and access attempts to identify anomalies that might indicate fraudulent activity. This can help flag suspicious logins, unusual purchase attempts, or automated bot attacks.
Threat Intelligence: AI can be used to analyze vast amounts of security data from various sources, including internal systems and external threat feeds. This allows for the identification of emerging threats and vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Risk Scoring: AI can be used to assign risk scores to transactions and user accounts based on various factors. This allows for implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) or additional verification steps for high-risk transactions.
Fraud Prevention: AI can be trained to identify patterns associated with fraudulent activities like credit card skimming, account takeovers, and fake accounts. This can help prevent financial losses and protect customer data.
Bot Detection and Mitigation: AI can be used to identify and block malicious bots that automate tasks like account creation, product scraping, and fraudulent transactions.
The true power lies in combining AI with traditional security measures. AI can analyze security logs to identify potential threats, which can then be investigated and addressed using traditional security tools. Additionally, AI can be used to continuously learn and adapt security measures as new threats emerge.
It's important to frame the solution around AI and human intelligence in digitally securing a firm as complementary rather than AI being inherently superior. While AI offers tremendous advantages, human expertise remains crucial for a well-rounded security posture.
Now we will dive into the necessary topic (i.e.,) e-commerce security dimensions. The categories that businesses need to consider to protect their website & customer information and ensure customer trust.
1. Confidentiality
It refers to protecting information from being accessed by an unauthorized person on the internet. Only the people who are authorized can gain access to view modify or use the sensitive data of any customer or merchant.
According to Juniper Research, nearly 146 billion records will be exposed by criminal data breaches between 2018 and 2023.
One confidentiality breach is sniffing. It's a program that steals all the important files of the company, individual identity or email messages, or personal reports of the internet user.
2. Integrity
We all have one common question, whether we have received the same data from the sender. Now it is the duty of integrity for the correctness of the information transmitted, received, or displayed on a website over the internet. Security measures like access controls and data validation help prevent unauthorized modification.
3. Availability
Customers expect the e-commerce platform to be accessible and operational whenever they need it. E-commerce businesses need to implement measures like system redundancy and disaster recovery plans to ensure high availability in case of outages or attacks.
4. Non-repudiation
Non-repudiation guarantees that the customer placed the order and the platform received it. Digital signatures and tamper-proof audit logs can help achieve non-repudiation. This ensures that a transaction or interaction cannot be denied by either party involved
5. Authentication
In e-commerce, since both the customer and seller need to trust each other, they must remain who they are in real life. Both the seller and buyer must provide proof of their original identity so that the e-commerce transaction can happen securely between them.
Example: Some users can use a fake email address to access any of the e-commerce services.
So, the Merchant perspective should be is the customer that I am communicating with a real person? If not, what could be their identity?
6. Privacy
Privacy is a major threat to any online transaction or internet user since personal information has been revealed and there is no way back to disclose it. Where confidentiality is a concern about the information present during communication, privacy concerns personal details.
Canva faced data breaches in 2019 that included the attack on users' information like name, email address, and more. for 139 million users.
A clear and concise privacy policy that outlines these practices is vital, along with features that give customers control over their data, such as opt-out options for marketing emails and the ability to request data deletion from the organization's database.
7. Risk Management
In e-commerce, the risk is ever associated with the transaction. Fraudulent transactions are one common risk where someone uses fake credentials to shop for an item.
Risk management involves identifying potential vulnerabilities and implementing measures to ensure a safe and trustworthy transaction between seller and buyer.
Example*: Two-factor authentication is one of the best ways to reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Second login authentication measures by confirming OTP sent to their email or mobile number other than a password.*
8. Compliance
The e-commerce platform must comply with legally relevant data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is crucial for protecting customer data and avoiding hefty fines.
An e-commerce platform that operates in Europe must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other data privacy laws.
9. Network Security
The network is a vital component of e-commerce security. Securing personal data and payment details, websites should have strong and secure network security protocols such as stateful firewalls combined with strong encryption practices, IDS (Intrusion Detection Systems), and WAFs (Web application firewalls).
10. Application Security
Developers should take responsibility for secure coding practices, vulnerability scanning, and penetration testing to identify and eliminate security risks. App security involves the practice of protecting e-commerce platforms and users from data breaches that arise due to e-commerce apps.
11. Physical Security
An overlooked aspect of e-commerce security. Physical security measures include access controls, surveillance cameras, and backup power supplies, to ensure that the data center remains secure and operational at all times.
Example*: An e-commerce platform may use a secure data center that requires biometric authentication and 24/7 surveillance to protect the physical infrastructure that supports the platform.*
12. Authorization
With authorization, a system can ensure that only authorized persons can access sensitive information like the payment process. As with other businesses, authorization is critical to identify user identity in e-commerce business transactions. It is about granting access to specific resources based on user identity.
Example: Suppose a customer tries to purchase using a credit card that is not theirs. The authorization process should detect that the customer is not the card owner and deny them access to the payment gateway.
Summary of 12 e-commerce security dimensions

Image courtesy of purchasecommerce.com
Building Trust in the Digital Age
Data security and customer privacy are not one-time achievements; they are ongoing commitments. By prioritizing these aspects and continuously adapting their security posture, e-commerce businesses can build trust with their customers and thrive in the digital age.
Cyber-attacks often happen that may affect anybody, but as an e-commerce business owner, you should not let your customers become victims of hacking or other attacks. By staying vigilant and adapting to new threats, e-commerce businesses can ensure a safe and trustworthy online shopping experience
The goal is to integrate AI and human intelligence being complementary forces in cybersecurity. By leveraging both, An e-commerce business can create a robust and adaptable security posture to safeguard customer data in the digital age.
So, a merchant has to make sure to prioritize e-commerce security. Together, we can make online transactions safe and secure for everyone.
"Trust is the foundation of everything good in life." - Stephen R. Covey. This quote holds true, especially in the world of e-commerce. By prioritizing data security and customer privacy, e-commerce businesses can build trust with their customers and create a secure and thriving online marketplace.